|
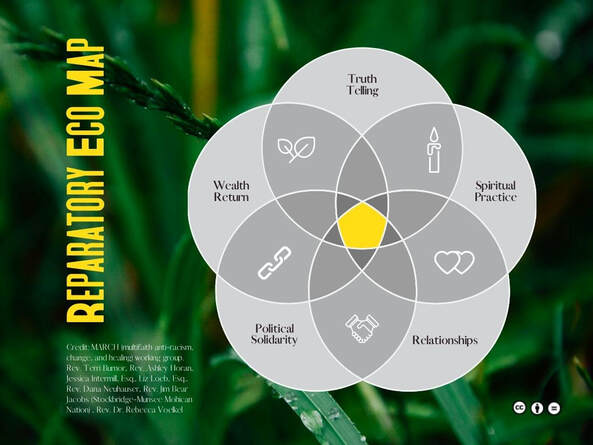
Rebecca Gonzalez-Campoy, Beloved Community Communications Team Session three of Minnesota Interfaith Power and Light’s (MNIPL) Reparations Learning Table generated discussion and reflection around how our faith community traditions or spiritual practices determine how we engage in meaningful repair work for the long haul. Take a look at the MARCH/Multifaith Anti-Racism Change and Healing Eco Map as a visual reminder of our reparations journey. Reparatory Eco Map credit: MARCH (multifaith anti-racism, change, and healing) Rev. Terri Burnor; Rev. Ashley Horan; Jessica Intermill, Esq.; Liz Loeb, Esq.; Rev. Dana Neuhauser; Rev. Jim Bear Jacobs (Stockbridge-Munsee Mohican Nation, Rev. Dr. Rebecca Voekel Learning about atrocities that our faith traditions committed against people of color may motivate us to abandon those communities. Yet, they can be the very place in which we find strength and support to engage in what Reparations Learning Table co-leader Jessica Intermill calls “the repentance/repair/return framework.”
This notion of lament, then repair and return of ill-gotten gains with penalty payment included, is a theme found in many faith traditions. The Biblical story of Zacchaeus the tax collector and Jesus (Luke 19:1-10 New International Version) is one of several examples. Aparigraha in the practice of yoga is the concept that nonpossession of things grounds you in the universe. Zen Buddhism teaches the ethics of not taking what is not given. Many Indigenous nations live by the code, “take only what you need.” It’s by no means a new concept. We’re just returning to it. The 7th Principle of Unitarian Universalism calls us to respect “the interdependent web of all existence of which we are a part.” The proposed 8th principle currently under consideration by the Unitarian Universalist Association — “journeying toward spiritual wholeness by working to build a diverse multicultural Beloved Community by our actions that accountably dismantle racism and other oppressions in ourselves and our institutions” — could be a call to lament, repair, and return land and resources to our Black and Indigenous neighbors. What does this action look like? And why do the work as a faith community? MNIPL Reparations Table co-leader Liz Loeb lifted up these reasons:
This is intergenerational work: elders possess wisdom that, when combined with the energy and new ideas of younger people, can create a stronger faith community committed to the spiritual practice of reparations, however they are defined. Here’s a personal example. I have an adopted, now estranged, Ojibwe brother who many in the Two Harbors, Minnesota, public education and law enforcement systems deemed lesser than the white kids, while growing up. When some believed that he could succeed, he did, but many teachers expected nothing from him. And that’s what they got. My brother wound up in juvenile detention for minor offenses. When he got out, the local sheriff typically went after him first when a crime occurred. I’m currently pursuing a master’s in divinity in UU Social Justice and completing my Community Pastoral Education (CPE) unit with Volunteers of America High School. There I provide whatever support staff needs to help mostly students of color who’ve been bounced out of the mainstream Minneapolis Public School system. My fellow Social Justice CPE cohort meets at Stillwater State Prison because that’s where half of our group lives. We are each trying to make the lives better for those who, for whatever reason, veered off the path to a healthy life. We are trying to return what was taken from the ancestors of our clients. I work with kids who have family members in prison, who are from immigrant families struggling to make their way in a completely foreign country, who’ve already been to juvenile detention, and/or who are members of gangs. Some will graduate. Some won’t. I could not do any of this work as an individual. Getting involved in Unity’s social justice work led me to pursue a master’s in divinity in UU Social Justice so that I may work in community to repent, repair, and return that which was ill-gotten. As Dr. Maya Angelou said, “Do the best you can until you know better. Then, when you know better, do better!” I leave you with prompts for reflection: What traditions or practices help ground you when you think about reparations as a lifelong commitment? What insight does your faith tradition or community of practice hold that feels relevant to reparations? For more information about reparations work, please visit these online resources: Minnesota Interfaith Power and Light Reparation actions from around the country Amicus Volunteers of America The Justice Database, a project of Unity Church
0 Comments
Leave a Reply. |
Topics
All
Beloved Community ResourcesUnity Justice Database
Team Dynamics House of Intersectionality Anti-Racism Resources in the Unity Libraries Collection Creative Writers of Color in Unity Libraries The History of Race Relations and Unity Church, 1850-2005 Archives
July 2024
Beloved Community Staff TeamThe Beloved Community Staff Team (BCST) strengthens and coordinates Unity’s antiracism and multicultural work, and provides opportunities for congregants and the church to grow into greater intercultural competency. We help the congregation ground itself in the understanding of antiracism and multiculturalism as a core part of faith formation. We support Unity’s efforts to expand our collective capacity to imagine and build the Beloved Community. Here, we share the stories of this journey — the struggles, the questions, and the collaborations — both at Unity and in the wider world.
The current members of the Beloved Community Staff Team include Rev. Kathleen Rolenz, Rev. KP Hong, Rev. Lara Cowtan, Drew Danielson, Laura Park, Lia Rivamonte and Angela Wilcox. |